Plain bearing bushes / brass / Thin-walled (Part Numbers - CAD Download)
- Volume Discount
- Order quantities extended (D-JIT)
- Stock
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
MPBZU40-30
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
- Technical Information
Back to the Category Plain Bearing Bushings
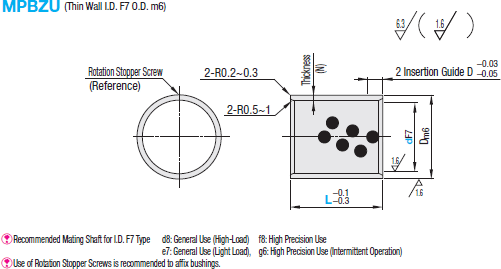
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More information.
Material: High Tensile Brass Alloy Solid Lubricant Embedded
Further specifications can be found under the tab More information.
| Part Number | - | L |
| MPBZU16 | - | 20 |
Plain bearing bushing, maintenance-free, selection details
- Material: sintered bronze, copper alloy with solid lubricant (Graphite), cast iron with solid lubricant, POM (polyacetal), PTFE (polytetraflouroethylene), composite steel, aluminum with fluoroplastic multi-coating
- Designs: straight, with collar, with housing and flange, with housing and block shape
- Housing coatings: nickel-plated, chrome-plated
- ISO tolerances: E7, G6, H7, h7, m6, r6
- Inner diameter [d]: 3 mm to 100 mm
- Outer diameter [D]: 4.6 mm to 120 mm
- Length [L]: 3 mm to 188 mm
- Permissible speed (max): 0.15 to 3.33 m/s
Description/Basics
Maintenance-free plain bearing bushings are suitable for linear and rotary motion. Movement is ensured by gliding. Thus, no rolling components are necessary, as with a rolling bearing.
Plain bearings can be selected in various shapes, materials and sizes at MISUMI. Bearing bushings are also already available integrated into the housing to make assembly easy and convenient.
Maintenance-free plain bearings have the benefit of not requiring maintenance or only little maintenance due to their integrated lubrication properties. This means that an external lubrication system can be omitted, which would not only require extra installation space, but is often very costly.
In contrast to rolling bearings, gliding bearings can generally accommodate high load-bearing capacities due to the larger contact area and require reduced installation space. The service life of the plain bearing bushings must be calculated depending on the application, since various influencing variables, such as roughness, stroke or rotational speed, have an influence on the service life.
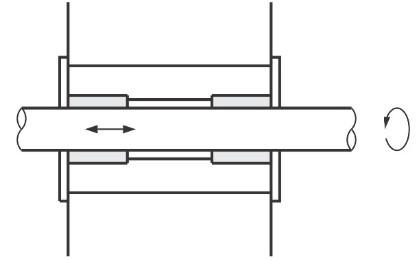
Application example: plain bearing bushing
Bearing types in comparison
| |||
|
|
| |
Plain bearing | Roller bearing | Roller bearing | |
Lubrication | without | required | required |
linear tables | suitable | well suitable | not suitable |
Rotational movement | suitable | not suitable | well suitable |
High load-carrying capacity | well suitable | not suitable | suitable |
Heat resistance | well suitable | not suitable | not suitable |
Corrosion resistance | suitable | not suitable | not suitable |
Wear resistance | Poor | well suitable | well suitable |
Space requirement | low | high | high |
Comparison Table - Plain bearing bushings, linear ball bushings, bearings
For more detailed information, please click on the More information tab
Function
The primary task of plain bearings is to guide and support shafts. The use of integrated lubricants significantly reduces friction and wear. The lubricants and materials of the plain bearing are always selected in such a way that the wear is specifically on the bearing bushing in order to protect the more expensive shaft from wear as much as possible.
The stored lubricants are released during operation. In most cases, it is released by heat and micro-abrasion. If the friction between the shaft and the plain bearing increases, the lubricant is released from the plain bearing and forms a protective lubricant film between the plain bearing and the shaft.
Sinter Bushings
A very common plain bearing is the plain bearing made of sintered metal. For this purpose, granules made of a copper alloy, such as brass or bronze, are heated and pressed into a sinter bushing. The pores of the sintered metal remain open through this process. The sintered bushing is then soaked in heated, liquid lubricant. During the cooling process of the lubricant, it solidifies and is stored in the pores of the sintered bushing.
Frictional heat conducts the lubricant embedded in the pores to the contact surface and forms a protective lubricant film between the gliding bearing bushing and the gliding partner.
Sinter bushings are often used in combustion engines because they have good emergency running properties. This property of the sintered metal plain bearings can also protect the shaft from damage in many other applications. If sintered slide bearings are consistently supplied with oil, these can also withstand very high speeds.
Example of a sinter bushing
Plain bearing with solid lubricant
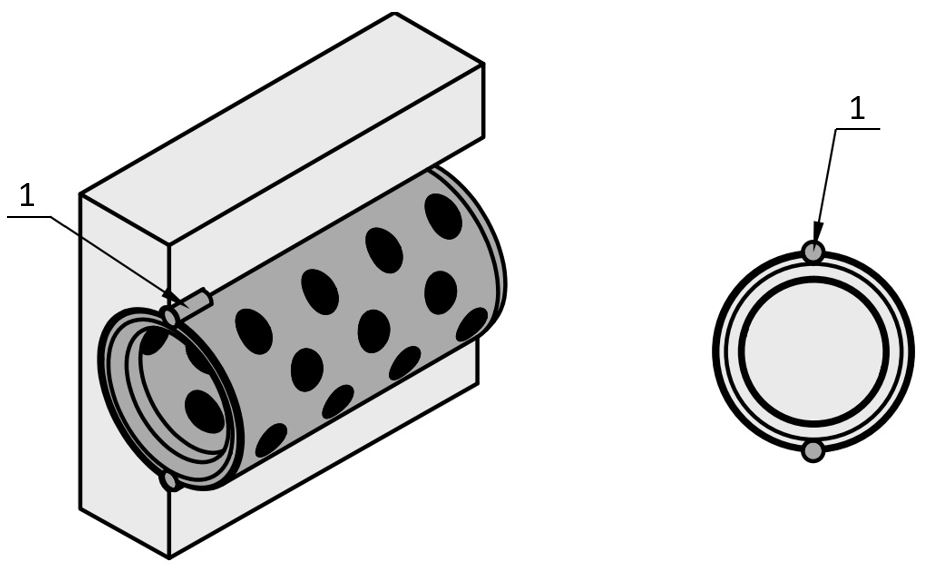
In the case of the plain bearings with solid lubricant, the included graphite ensures the lubrication of the contact surface. Solid lubricant has good lubrication properties, especially at high pressures and higher temperatures. Micro-abrasion releases graphite particles from the bearing bushing lubrication pockets and directs them to the contact surface.
The positions of the solid lubricant bearings (1) allow for the most uniform lubrication possible and thus ensure a low friction value and reduced wear.
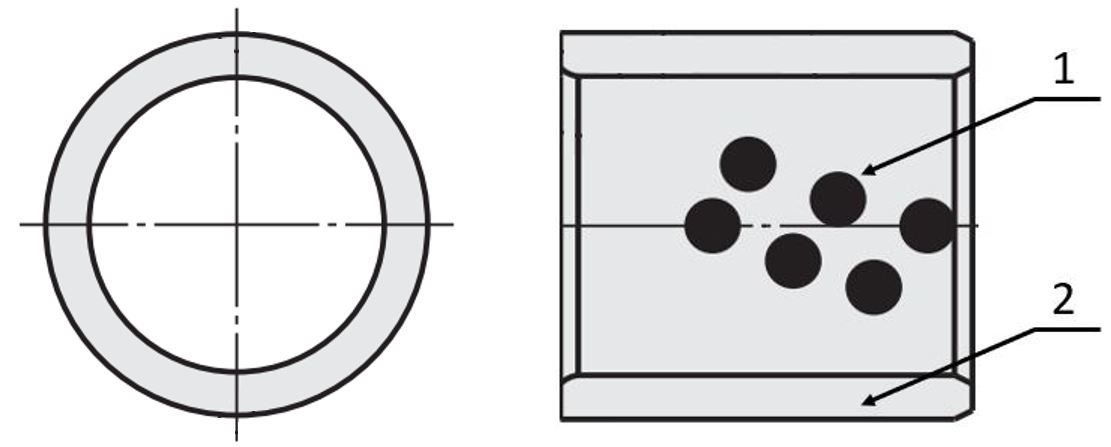
(1) Solid lubricant, (2) plain bearing bushing
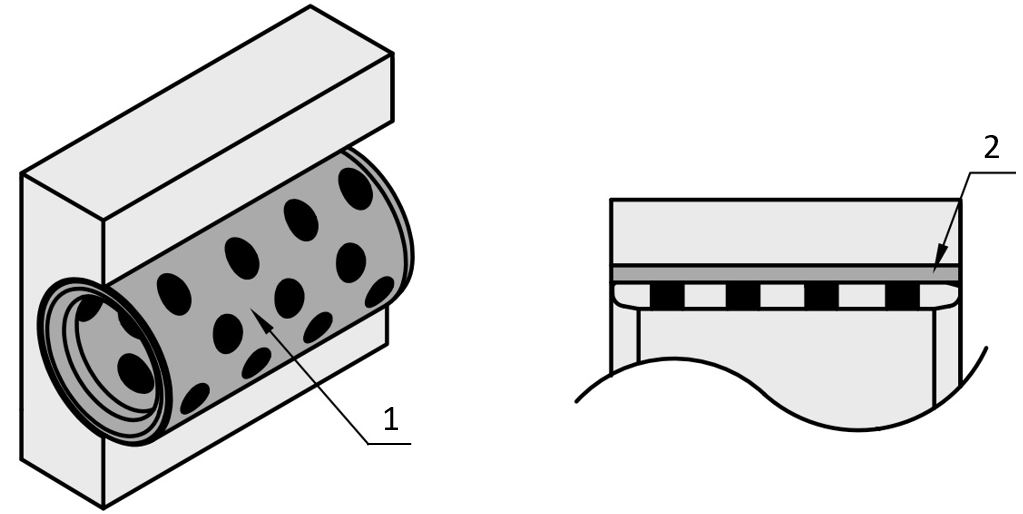
MISUMI also offers plain bearing bushings with solid lubricant with an integrated thrust washer. The integrated thrust washer is a flange with solid lubricant. These collar bushings can also be used to protect a gear wheel or shaft shoulder from wear. At the same time, an additional thrust disc can be dispensed with, which reduces the variety of parts and simplifies assembly and maintenance. These advantages of the collar bushing allow for use as an axial sliding bearing.
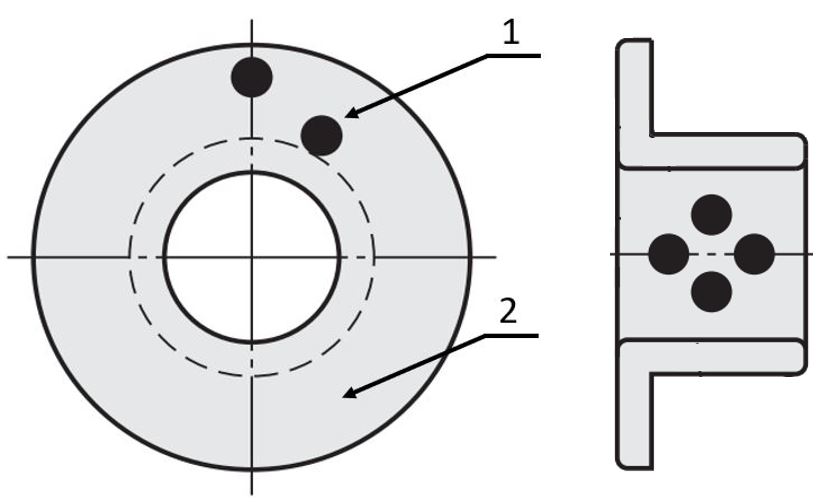
(1) Solid lubricant, (2) plain bearing bushing
Plain bearings made of plastic
Plain bearings made of plastic have a good chemical resistance. They are also well suited for locations in a corrosive environment. The applied plastics have principally good gliding properties, which can additionally be improved by additives. Contrary to the conventional flange bushing, plastic plain bearings can also be combined with aluminum shafts.
Plastic plain bearings are relatively cost-effective and light. Therefore, they are used in many areas, often in small devices such as printers or hinge elements.
At very high speeds, plastic bearing bushings can burn out or melt due to the resulting frictional heat. Therefore, it is particularly important to maintain the maximum speeds of rotation and ambient temperatures in plastic plain bearings. At higher speeds of rotation and bearing powers, a metallic plain bearing is usually used.
Plain bearings made of composite material
Plain bearings made of composite material consist of a metallic base carrier and a plastic layer applied on the inside. Due to the metallic outer ring, plain bearings made of composite material are generally more stable than plastic plain bearings. Nevertheless, they do not have to forego the advantages (chemical resistance, etc.) of the plastic.
Some plain bearings are provided with an additional composite layer made of sintered bronze. This is inserted between the metallic outer ring and the inner ring made of plastic, which ensures an additional emergency running property if the plastic is closed. Sliding bearing bushings with a PTFE composite layer can withstand temperatures up to 280°C and thus work in a high temperature range than conventional plastic plain bearings (approx. 80°C).
Plain bearings with a collar or without a collar made of composite material have a very thin-walled design and are therefore very space-saving.
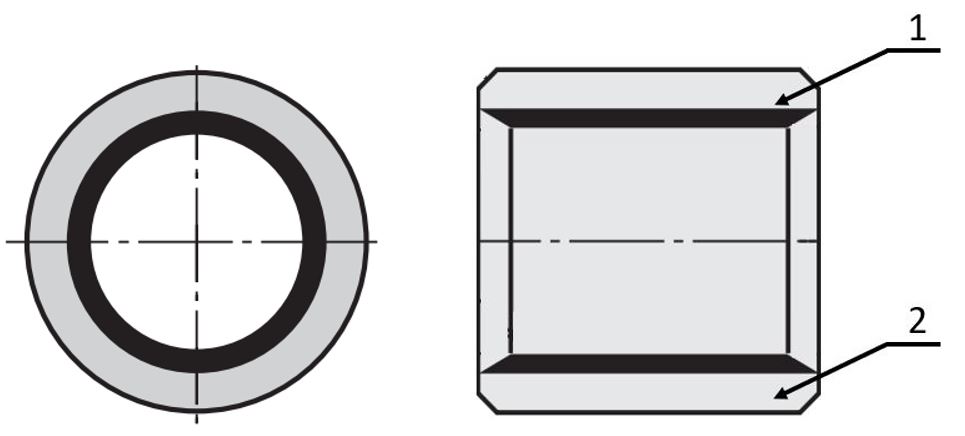
(1) Plastic/composite layer, (2) metal base carrier
Plain bearings with housing
All previously mentioned plain bearings are already available from MISUMI mounted in housings (flange housings or block housings). This reduces the assembly time significantly.
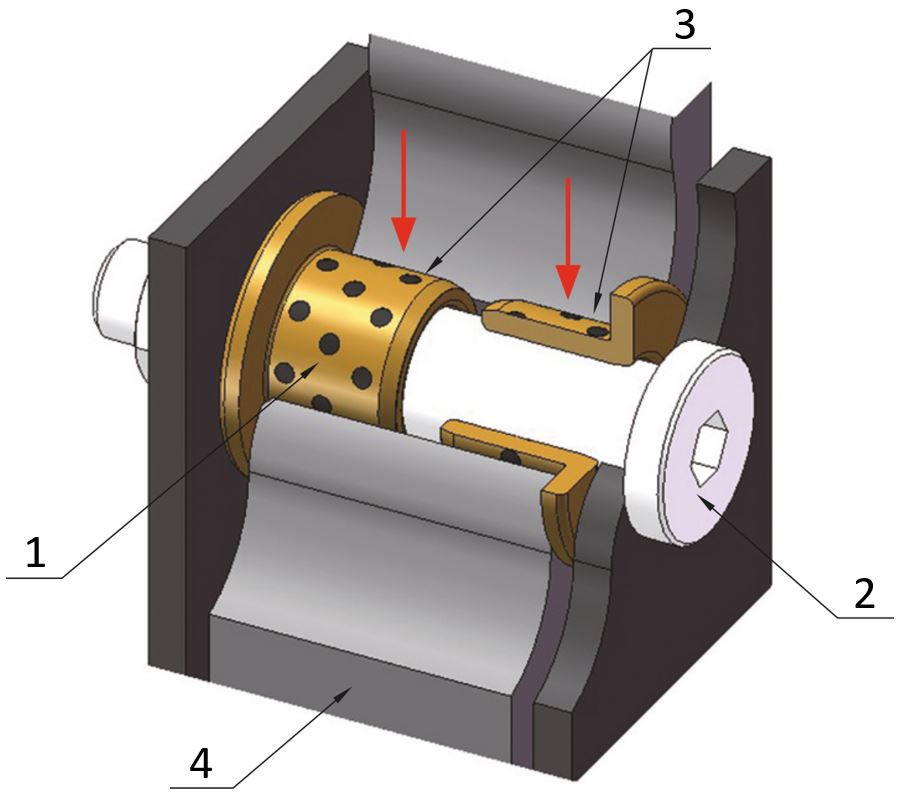
In addition, the housing units have the additional advantage that they are available with a contact seal or contactless seal (1). The contact seal prevents small dust particles from getting onto the gliding surface of the plain bearing. The contactless seal design prevents large debris from entering while reducing the gliding resistance compared to the contact seal design.
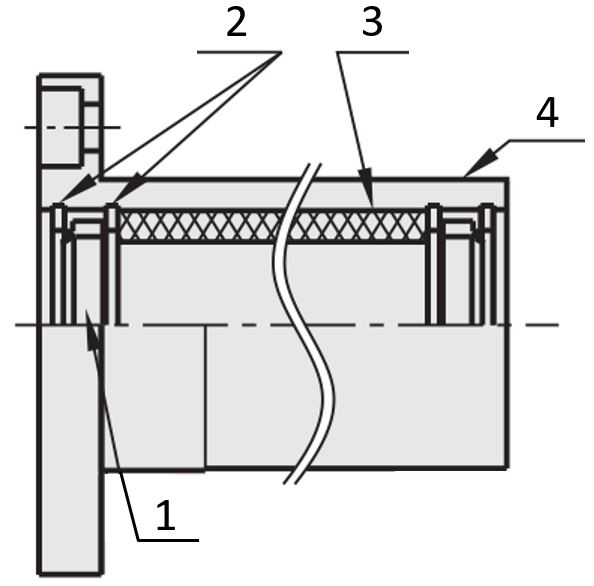
(1) Seal, (2) retaining rings, (3) maintenance-free plain bearing, (4) housing
Areas of Application
Maintenance-free plain bearings are suitable for linear and rotary motion. They are used in many applications, from simple hinged mechanisms to precise linear guides. Due to their versatility, plain bearings are indispensable in various industries of mechanical engineering and plant engineering.
Due to their large contact surface, plain bearings can generally accommodate high loads. Compared to rolling bearings, plain bearings are also quieter, require less maintenance and are less susceptible to contamination.
Collar bushings with solid lubricants can also serve as axial plain bearings, since MISUMI offers flange bushings with integrated solid lubricants.
Bearing bushings require reduced installation space. Therefore, plain bearings are used in applications in which rolling bearings are not possible due to limited installation space.
A particularly space-saving and thin-walled plain bearing offered by MISUMI is type MPBZU.
Materials
MISUMI plain bearings are available in the following material compositions:
- Sintered bronze
- Copper alloy with solid lubricant (Graphite)
- Cast iron with solid lubricant
- POM (polyacetal)
- PTFE (polytetraflouroethylene)
- Steel with multi-coating
- Aluminum with fluoroplastic multi-coating
Dimensions
Maintenance-free plain bearings are available in many dimensions at MISUMI:
- ISO tolerances: E7, G6, H7, h7, m6, r6
- Inner diameter [d]: 3 mm to 100 mm
- Outer diameter [D]: 4.6 mm to 120 mm
- Length [L]: 3 mm to 188 mm
Shaft Tolerance
Shaft tolerance is used to create the clearance between the plain bearing bushing and the shaft. Which shaft tolerance is recommended for a plain bearing with a plain bearing bushing depends on the application and required precision. MISUMI offers plain bearings in the ISO tolerances E7, G6 and H7. For particularly precise applications, MISUMI also offers linear shafts in the ISO tolerances g6 and f8.
Surface Roughness
The surface roughness of the shaft has a major impact on the wear of the plain bearing bushing. In order to reduce wear, a uniformly ground shaft is recommended as a gliding partner. A good roughness of approx. 0.4 to 1.6 μm contributes to a good glide and low wear.
Instructions for use
Design | Properties | Shapes |
Copper alloy | • High temperature resistance | • straight |
Sintered bronze | • Resistant to friction welding | • straight |
Cast steel | • Ideal for medium loads and low speeds of rotation | • straight |
Multi-coating | • High temperature resistance | • straight |
Plastic | • High temperature resistance (PTFE) | • straight |
Comparison Table - Plain Bearing Sleeve Versions
For more information on material properties, environmental conditions, and mechanical properties, see this PDF.
Installation Information
Press-in
Maintenance-free plain bearing bearings (2) must be carefully pressed into a housing with a vice or press (press fit). To facilitate this process, the edge of the inner diameter of the housing is chamfered (1). It is recommended to apply a small amount of lubricant to the housing (3). If the housing fit is too tight, this can affect the inner diameter of the maintenance-free sliding bearing and lead to increased wear. You can find the suitable housing tolerance for the respective plain bearing under the tab More Information.

(1) Phase, (2) plain bearing bushing, (3) housing
Turning Stop Screw
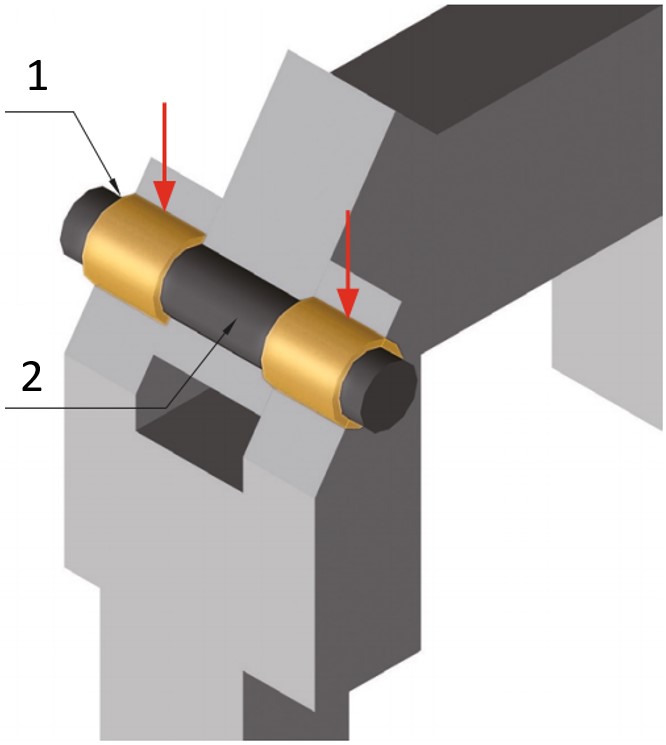
An undesired rotation of a maintenance-free plain bearing bushing can be prevented with a turning stop screw (1) (press fit/transition fit). The use of a rotation stop screw (1) is recommended for high loads, rotational speeds and temperatures.
(1) Turning stop screw
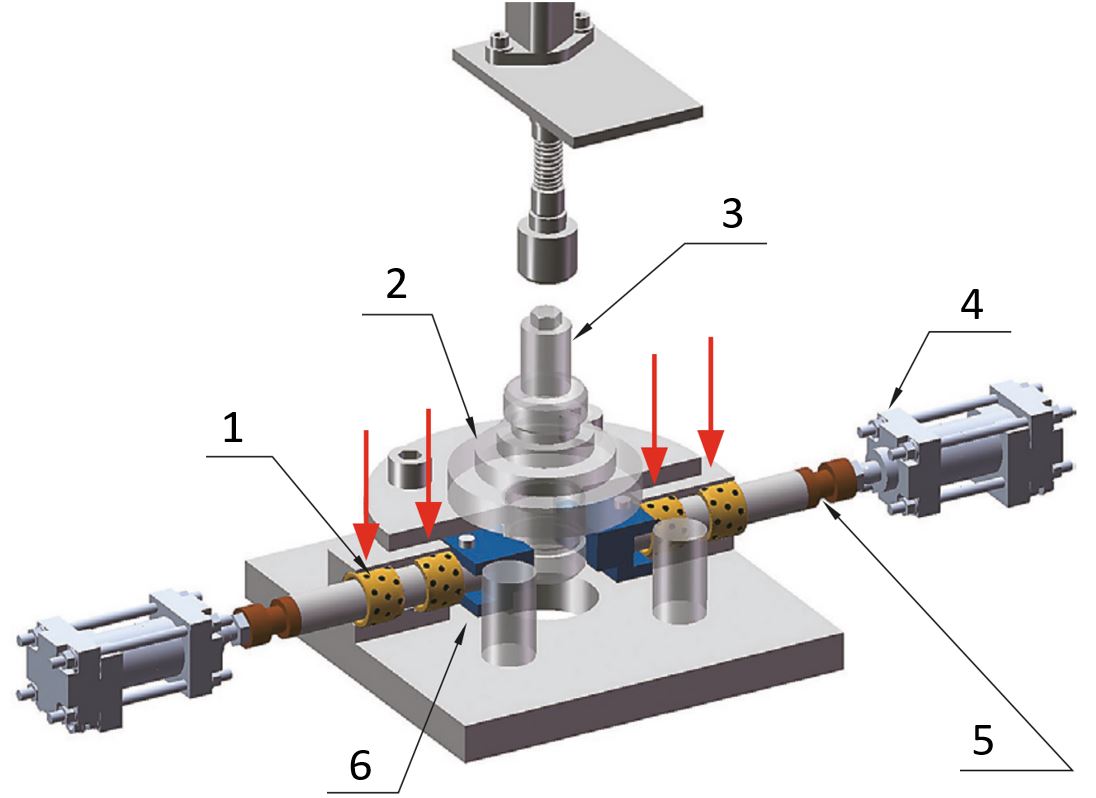
Bonding
If for various reasons you cannot use of a rotation stop screw, a maintenance-free sliding bearing bushing can be glued (2) into the housing with adhesive (play fit). Depending on the external influences, this can be done with Loctite. For applications that require high precision, this variant is not recommended due to the positioning accuracy.
(1) Plain bearing bushing, (2) adhesive layer

_M0101000000.jpg)
Adjusting rings/clamping rings
_M0103000000_.jpg)
_M0102000000_.jpg)





Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
Part Number
|
|---|
| MPBZU40-30 |
| Part Number |
Standard Unit Price
| Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | I.D. d (mm) | O.D. D (mm) | Overall Length L (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
21.28 € | 1 | Available | 5 Days | 10 | 40 | 45 | 30 |
Loading...
Back to the Category Plain Bearing Bushings

Overview of the various designs as PDF
| Part Number | L | Dm6 | Thickness (N) | Housing Dia. (Recommended Dimension) | Rotation Stopper Screw (Reference) | |||||||||||||
| Type | dF7 | Ref. Dim. | Tolerance (H7) | |||||||||||||||
| MPBZU | 5 | +0.022 +0.010 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 7 | +0.015 +0.006 | 1 | 7 | +0.015 0 | M4x8 | |||||||
| 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 8 | 8 | |||||||||||
| 8 | +0.028 +0.013 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 10 | 10 | |||||||||
| 10 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 12 | +0.018 +0.007 | 12 | +0.018 0 | |||||||
| 12 | +0.034 +0.016 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 1.5 | 15 | ||||||||
| 13 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 16 | 16 | ||||||||||
| 15 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 18 | 18 | |||||||||
| 16 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 20 | +0.021 +0.008 | 2 | 20 | +0.021 0 | ||||||
| 18 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 22 | 22 | M5x8 | |||||||||
| 20 | +0.041 +0.020 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 24 | 24 | |||||||||
| 25 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 29 | 29 | ||||||||||
| 30 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 34 | +0.025 +0.009 | 34 | +0.025 0 | M6x16 | |||||||
| 35 | +0.050 +0.025 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 40 | 2.5 | 40 | ||||||||||
| 40 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 45 | 45 | |||||||||||
| 50 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 55 | +0.030 +0.011 | 55 | +0.030 0 | M8x16 | ||||||||||
| d | Dimension Variation | Thin Wall MPBZU | Standard Type MPBZ | |||
| O.D. Dm6 | Thickness (N) | O.D. Dm6 | Thickness (N) | O.D. Dm6 | Thickness (N) | |
| 5 | -2 | -1 | 7 | 1 | 9 | 2 |
| 6 | -2 | -1 | 8 | 10 | ||
| 8 | -2 | -1 | 10 | 12 | ||
| 10 | -2 | -1 | 12 | 14 | ||
| 12 | -3 | -1.5 | 15 | 1.5 | 18 | 3 |
| 13 | -3 | -1.5 | 16 | 19 | ||
| 15 | -3 | -1.5 | 18 | 21 | ||
| 16 | -2 | -1 | 20 | 2 | 22 | |
| 18 | -2 | -1 | 22 | 24 | ||
| 20 | -4 | -2 | 24 | 28 | 4 | |
| 25 | -4 | -2 | 29 | 33 | ||
| 30 | -4 | -2 | 34 | 38 | ||
| 35 | -4 | -2 | 40 | 2.5 | 44 | 4.5 |
| 40 | -5 | -2.5 | 45 | 50 | 5 | |
| 50 | -7 | -3.5 | 55 | 62 | 6 | |
Basic information
| Type | Straight | Metallic | High-Tensile Brass Alloy | Maximum Allowable PV Value Range(N/mm2•m/s) | 1.1 to 2.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Allowable PV Value(N/mm²·m/s) | 1.65 | Max. Allowable Surface Pressure P(N/mm2) | 29 | Max. Allowable Velocity V(m/s) | 0.5 |
| Mounting Hole Fits | H7 | Operating Temperature Range(°C) | -40::150 |
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Type
- MPBZU
-
I.D. d(mm)
-
O.D. D(mm)
-
Overall Length L(mm)
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- Same day
- 5 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Complementary Products
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry