- [D] Diameter (Shaft)(mm)
- 6
- 8
- 10
- 12
- 13
- 15
- 16
- 18
- 20
- 25
- 30
- 35
- 40
- 50
- [L] Length (Shaft)(mm)[20–1500/1mm jedn.]
- Material
- Unalloyed Steel
- EN 1.1191 Equiv.
- Stainless Steel (austenitic)
- EN 1.4301 Equiv.
- Alloyed Steel
- EN 1.3505 Equiv.
- Stainless Steel (martensitique)
- EN 1.4037 Equiv.
- Heat Treatment
- Surface Treatment
- [F] Length (stud - offset - front side)(mm)[0–750/1mm jedn.]
- CAD
- 2D
- 3D
- Szacowane dni wysyłki
- Wszystko
- W ciągu 4 dni robocze
- W ciągu 6 dni robocze
- W ciągu 7 dni robocze
- W ciągu 12 dni robocze
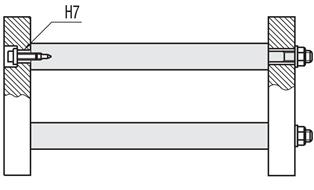
Linear shafts / keyway on one side
Numer części:
.Rysunek konturowy i tabela specyfikacji
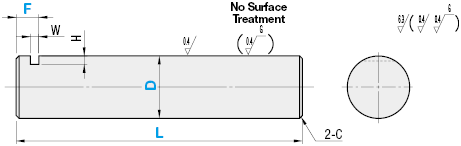
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D Tol. | |||
| D | g6 | h5 | f8 |
| 6 | -0.004 -0.012 | 0 -0.005 | -0.010 -0.028 |
| 8 | -0.005 -0.014 | 0 -0.006 | -0.013 -0.035 |
| 10 | |||
| 12 | -0.006 -0.017 | 0 -0.008 | -0.016 -0.043 |
| 13 | |||
| 15 | |||
| 16 | |||
| 18 | |||
| 20 | -0.007 -0.020 | 0 -0.009 | -0.020 -0.053 |
| 25 | |||
| 30 | |||
| 35 | -0.009 -0.025 | 0 -0.011 | -0.025 -0.064 |
| 40 | |||
| 50 | |||
Further specifications can be found under the tab More Information.
| Part Number | - | L | - | F |
| SFAK16 | - | 265 | - | F25 |
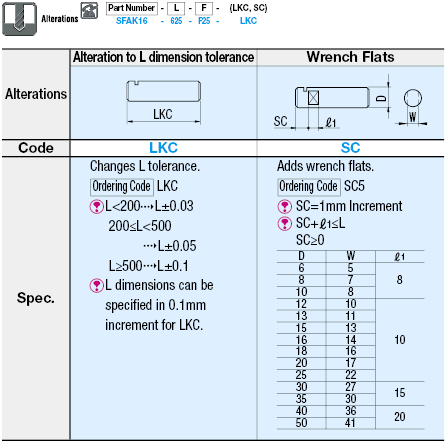
You find further options in detail under Option Overview.
Lista numerów części
| Numer części |
|---|
Cena jednostkowa (bez VAT)(Cena jednostkowa z podatkiem) | Standardowa data wysyłki |
|---|
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 6 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 7 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
- ( - ) | 4 dni robocze |
Szczegółowe informacje
Podstawowe informacje
Przestroga
- SFAK has been localized according to European needs and requirements. Please have a look on the EU version SFAKEU. SFAKEU is available in EN 1.1213 (Cf53) and h6 / h7.
Kontury i specyfikacja

Overview of the shaft designs as PDF
| Part Number | 1mm Increment | W | H | C | |||
| Type | D | L | F | ||||
| (D Tolerance g6) SFAK SSFAK PSFAK PSSFAK RSFAK (D≤30, L≤500) (D Tolerance f8) PSFGK PSSFGK | (D Tolerance h5) SFUK SSFUK PSFUK PSSFUK | 6 | 20~600 | 5≤F≤L/2 | 3.1 | 2 | 0.5 or Less |
| 8 | 20~800 | ||||||
| 10 | 20~800 | 3 | |||||
| 12 | 20~1000 | ||||||
| 13 | 25~1000 | ||||||
| 15 | 25~1200 | ||||||
| 16 | 30~1200 | ||||||
| 18 | 30~1200 | ||||||
| 20 | 30~1200 | 4 | 1.0 or Less | ||||
| 25 | 35~1200 | 5 | |||||
| 30 | 35~1500 | 7≤F≤L/2 | 5.1 | 6 | |||
| 35 | 35~1500 | 7 | |||||
| 40 | 50~1500 | 8 | |||||
| 50 | 65~1500 | 10 | |||||

You find further options in detail under Option Overview.
Surface Limits / Hardness - Linear Shafts
Limits of hardness and hardening depth
The linear shafts are processed after the base material has undergone inductive hardening. Therefore, the processed surfaces may result in a deviating hardness.
In the following example, you can view the affected areas of the linear shaft, which may be affected after processing by e.g. threads, level surfaces, key surfaces and transverse bores.
_(450x164).jpg)
Cause for deviating hardness
The raw material of the linear shaft is treated via thermal induction before grinding. Thus, a configured linear shaft can be custom-made not only cost-effectively, but also with short delivery times. The linear shaft is hardened at the boundary layer (boundary layer hardening) of the liner shaft. The depth of the hardened boundary layer depends on the material used and the diameter of the linear shaft. The following table shows the hardening depth of linear shafts.
Coatings and plating are applied to the raw material after hardening and grinding. For more information, see Coatings of the Linear Shaft.
.jpg)
Figure of boundary layer hardening: hardened boundary layer in light gray
Effective hardening depth of linear shafts
| Outside diameter (D) | Effective hardening depth | |||
| EN 1.1191 equiv. | EN 1.3505 equiv. | EN 1.4125 equiv. | EN 1.4301 equiv. | |
| 3 | - | +0.5 | +0.5 | Without induction hardening |
| 4 | - | |||
| 5 | - | |||
| 6 - 10 | +0.3 | |||
| 12 - 13 | +0.5 | +0.7 | +0.5 | |
| 15 - 20 | +0.7 | |||
| 25 - 50 | +0.8 | +1 | ||
Overview of the effective hardening depth as PDF
Coatings of the linear shaft
The surface coating is applied to the raw material before machining the linear shaft. Thanks to their coating, the usable surface or work surface of the linear shaft is not only protected against corrosion but also against wear.
Machined positions of the linear shafts, such as plane surfaces or threads, may be uncoated, as they are added afterwards. This can lead to the machined surfaces being corroded in a linear shaft made of steel. If the linear shaft is used in a corrosive environment, it is recommended to use a stainless steel linear shaft.
The following figure shows the areas of the linear shaft that are coated (crosshatched).
_(321x64).jpg)
Figure: Coating of linear shafts
You can find further information on surface treatment and hardness in this PDF .
General Information - Linear Shafts
Linear Shaft Selection Details
- Material: steel, stainless steel
- Coating/plating: uncoated, hard chrome plated, LTBC coated, chemically nickel-plated
- Heat treatment: untreated, inductively hardened
- ISO tolerances: h5, k5, g6, h6, h7, f8
- Precision classes: perpendicularity 0.03, concentricity (with thread and increments) Ø0.02, perpendicularity 0.20, concentricity (thread and stepper) Ø0.10
- Linearity/roundness: depends on diameter, here for the PDF
Description / basics of the linear shaft
Linear shafts are steel shafts that perform guiding tasks in combination with linear bearings, such as plain bearing bushings or linear ball bushings. Linear shaft holding functions can be adopted from shaft holders or linear ball bearing adapters. Most linear shafts are heat-treated (induction hardened) solid shafts. A special design of linear shafts is the hollow shaft, which is also called tubular shaft. Inductively hardened linear shafts have a high surface hardness and a tough core. The achievable surface hardness is approx. 55-58 HRC (see information on hardening depth). Linear shafts made of stainless steels can generally not be hardened. Therefore, these steel shafts should be chrome plated to protect them from wear.
Materials
Linear shafts are mainly hardened steel shafts. In addition to the selected heat treatment, the steel used in particular imparts its properties to the linear shaft, although it is a hollow shaft or a solid shaft. Therefore, special aspects such as hardness, corrosion and wear must be considered when selecting the shaft steel.
Coatings
To protect linear shafts from corrosion, the surface can be chemically nickel-plated. As an alternative to chemical nickel-plating, steel shafts can also be coated with LTBC. The LTBC coating is an anti-corrosive surface coating and it is a low-reflection coating, made of a 5 μm thick film of fluoropolymer, which in essence is a black film. In addition, the LTBC coating is resistant to bursting pressure by extreme or repeated bending. LTBC-coated linear shafts are thus particularly suitable for locations where corrosion or light reflections are undesirable. Linear shafts that require particularly high surface hardness and wear resistance can be hard chrome plated.
Function
The form and function of linear shafts differ from linear guiderails. Linear guiderails are square rails that work in combination with carriers (rotary elements, carriages) according to the rolling or sliding principle. Linear shafts on the other hand are precision-ground round steel shafts that take on a linear guide function in conjunction with linear ball bushings or plain bearing bushings (maintenance-free bushings).
Areas of Application
Linear shafts are intended for axial motion. Whether horizontal or vertical linear motion, all linear motions can be implemented with linear shafts. Common applications are stroke mechanisms and other applications with high demands on smoothness, precision and service life. Linear shafts can therefore be used in almost all industries of plant construction and mechanical engineering. Linear shafts are often found in 3D printers, metering equipment, measuring devices, positioning devices, alignment devices, bending devices and sorting equipment.
Instructions for Use / Installation - Linear Shafts
For product selection, please observe the linear shaft tolerances (e.g. h5, k5, g6, h6, h7, f8) in conjunction with the diameter tolerance of the plain bearing bushing (sliding bearing) after pressing in or the running circle diameter of the linear ball bearing (ball bushing).
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

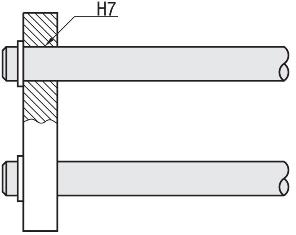
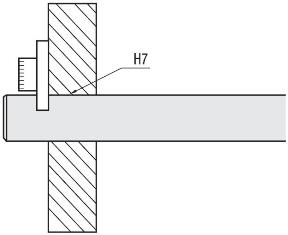
_M0102000000_.jpg)
Adjusting rings/clamping rings
_M0103000000_.jpg)
_M0104000000.jpg)
_M0107080000.jpg)
_M0105000000.jpg)




